Jacob MBBS MS Anatomy in Human Anatomy 2008 The sympathetic trunk. The thyroid cartilage is a hyaline cartilage structure that sits in front of the larynx and above the thyroid glandThe cartilage is composed of two halves which meet in the middle at a peak called the laryngeal prominence also called the Adams apple.
Posterior Grey Column Wikipedia
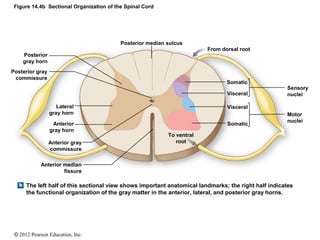
Indicates the anatomical organization of sensory tracts in the posterior white column for comparison with the organization of motor nuclei in the anterior gray horn.
. The sympathetic trunks see Figs 325 326 lie on each side of the vertebral column extending from the base of the skull to the coccyx where the two chains fuse togetherEach trunk contains a number of sympathetic ganglia the thoracic region having about 11 ganglia which lie on the neck of the ribs. In the midline above the prominence is the superior thyroid notchA counterpart notch at the bottom of the cartilage is. The anterior and posterior roots merge just before the intervertebral foramen and form the trunk of the spinal nerve.
Just above the tubercles the posterior aspect of the medulla is occupied by a triangular fossa which forms the lower part of the floor of the fourth ventricle. The posterior cingulate cortex PCC forms part of the posteromedial cortex. The inferior temporal horn is the largest component of the lateral ventricleIt begins at the posterior end of the central region and runs anteroinferiorly into the temporal lobe.
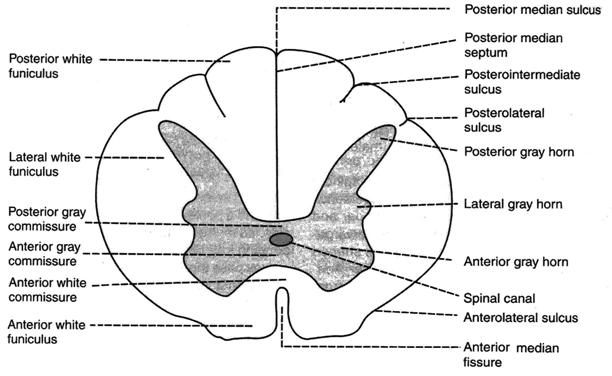
They originate from the posterior horns of gray matter and exit through the posterolateral sulcus of the spinal cord. The grey column refers to a somewhat ridge-shaped mass of grey matter in the spinal cord. The fasciculi end in rounded elevations known as the gracile and cuneate tubercles.
Almost all of behavior involves motor function from talking to gesturing to walking. It is highly anatomically connected Hagmann et al 2008 has a high baseline metabolic rate Raichle et al 2001 and is a central part of the default mode network DMN Buckner et al 2008Despite its importance in health and disease the PCC is notably absent from many. Superior colliculusinferior colliculusperiaquaductal grayred nucleussubstantia nigra Brainstem inferior olivespinal cord Cerebellum cerebellar hemispherehorizontal fissure Vascular structures.
The posterior roots transmit sensory information and have sensory ganglion attached to them. Note that both sensory and motor components of the spinal cord have a definite regional organization. But even a simple movement like reaching out to pick up a glass of water can be a complex motor task to study.
The two-layered model of TLF recognizes a posterior layer surrounding the posterior aspect of the paraspinal muscles and an anterior layer lying between the paraspinal muscles and the QL Fig. The two-layered model has been presented in the early English versions of Henry Grays work Gray 1923 and from the first American edition Gray 1870 to the 30th. It has an anterior end that reaches close to the uncus of the cerebrum a floor and a roofThe roof of the inferior horn is formed mainly by the tapetum of the corpus callosum and the cauda of.
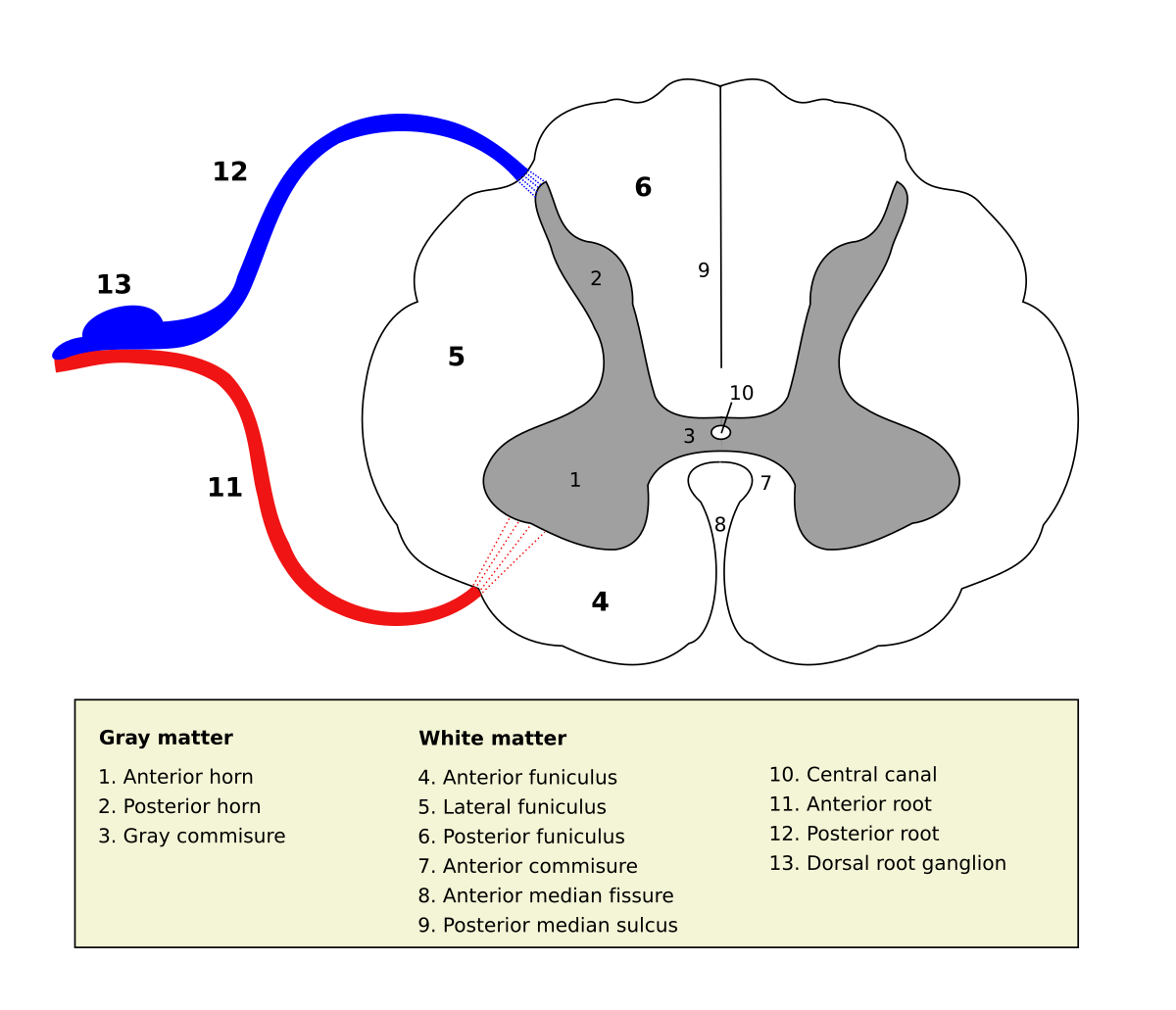
Not only does your brain have to figure out which muscles to contract and in which order to steer your hand to the glass it also has to estimate the force needed to pick up the glass. Posterior white column funiculus Anterior white Anterior white. Gray commisure sic in the image to the right all of which are visible in cross-section of the spinal cord.
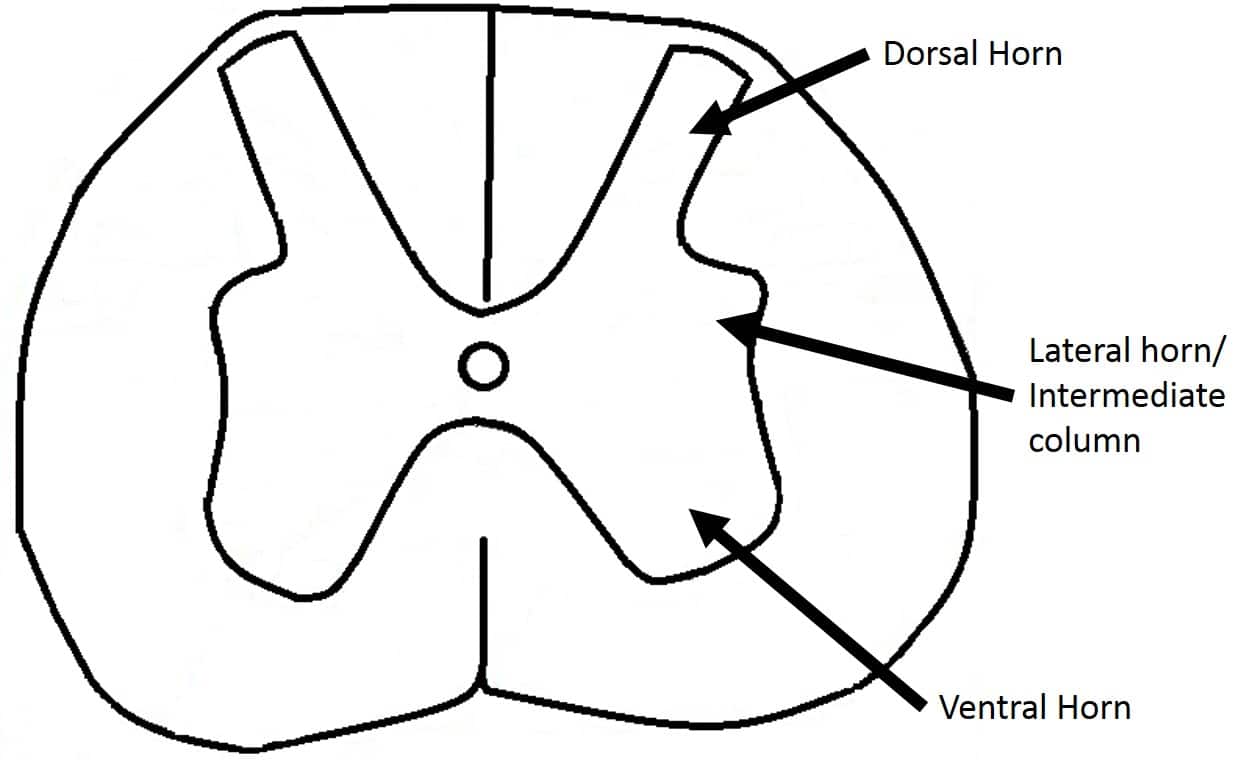
The anterior grey column the posterior grey column and the lateral grey column labeled 3. This presents as three columns. They are caused by masses of gray matter known as the nucleus gracilis and the nucleus cuneatus.

Lab 8 Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet

14 4 The Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology

0 comments
Post a Comment